MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules with Answers
Question 1.
During acetylation of glucose it needs ,v moles of.acetic anhydride. The value of x would be
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 4
(d) 1
Answer
Answer: (b) 5
Question 2.
On oxidation with a mild oxidising agent like Br2/H20, the glucose is oxidized to
(a) saccharic acid
(b) glucaric acid
(c) gluconic acid
(d) valeric acid
Answer
Answer: (c) gluconic acid
Question 3.
Invert sugar is
(a) a type of cane sugar
(b) optically inactive form of sugar
(c) mixture of glucose and galactose
(d) mixture of glucose and fructose in equimolar quantities
Answer
Answer: (d) mixture of glucose and fructose in equimolar quantities
Question 4.
Which of the following compounds is found abundatly in nature?
(a) Fructose
(b) Starch
(c) Glucose
(d) Cellulose
Answer
Answer: (b) Starch or (d) Cellulose
Question 5.
Glycosidic linkage is an
(a) amide linkage
(b) ester linkage
(c) ether linkage
(d) acetyl linkage
Answer
Answer: (c) ether linkage
Question 6.
Starch is composed of two polysaccharides which arc
(a) amylopectin and glycogen
(b) amylose and gtycogen
(c) amylose (20%) and amylopectin (80%)
(d) cellulose and glycogen
Answer
Answer: (c) amylose (20%) and amylopectin (80%)
Question 7.
Which reagent is used to convert glucose into saccharic acid?
(a) Br2/H2O
(b) Nitric acid
(c) Alkaline solution of iodine
(d) Ammonium hydroxide
Answer
Answer: (b) Nitric acid
Question 8.
Maltose is made up of
(a) two α-D-glucose
(b) normal β-D-glucose
(c) α- and β-D-glucose
(d) fructose
Answer
Answer: (a) two α-D-glucose
Question 9.
What is the basic formulae for starch?
(a) (C6H12O6)n
(b) (C6H10O5)n
(c) C12O12O11
(d) (C6H12O4)n
Answer
Answer: (b) (C6H10O5)n
Question 10.
Whicn of the following is an example of an aldopentose?
(a) D-Ribose
(b) Glyceraldehyde
(c) Fructose
(d) Erythrose
Answer
Answer: (a) D-Ribose
Question 11.
![]()
Identify Z.
(a) 2-lodoheptane
(b) Heptane-2-ol
(c) 2-lodohexane
(d) Heptanoic acid
Answer
Answer: (d) Heptanoic acid
Question 12.
Which of the following treatment will convert starch directly into glucose?
(a) Heating with dilute H2SO4
(b) Fermentation by diastase
(c) Fermentation by zymase
(d) Heating with dilute NaOH
Answer
Answer: (a) Heating with dilute H2SO4
Question 13.
The general formula of carbohydrates is
(a) CnH2n+1O
(b) CnH2nO
(c) Cx(H2O)
(d) Cn(H2,O)2n
Answer
Answer: (c) Cx(H2O)
Question 14.
The a-and p-forms of glucose are
(a) isomers of D (+) glucose and L (-) glucose respectively
(b) diastereomers of glucose
(c) anomers of glucose
(d) isomers which differ in the configuration of C-2
Answer
Answer: (c) anomers of glucose
Question 15.
What are the hydrolysis products of sucrose?
(a) Fructose + Fructose
(b) Glucose + Glucose
(c) Glucose + Galactose
(d) D-Glucose + D-Fructose
Answer
Answer: (d) D-Glucose + D-Fructose
Question 16.
Carbohydrates are stored in human body as the polysaccharide
(a) starch
(b) glycogen
(c) cellulose
(d) amylose
Answer
Answer: (b) glycogen
Question 17.
The glycosidic linkage involved in linking the glucose units in amylose part of starch is
(a) C1-C4 β-linkage
(b) C4-C6 β-linkage
(c) C1-C6 α-linkage
(d) C1-C4 α-linkage
Answer
Answer: (d) C1-C4 α-linkage
Question 18.
The conversion of maltose into glucose is possible by the enzyme
(a) zymase
(b) lactase
(c) maltase
(d) diastase
Answer
Answer: (c) maltase
Question 19.
Which of the following is a non-reducing sugar?
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Maltose
(d) Lactose
Answer
Answer: (b) Sucrose
Question 20.
Which one of the following is not correct?
(a) D(-) Fructose exist sin furanose structure
(b) D (+) Glucose exists in pyranose structure
(c) In sucrose the two monosaccharides are held together by peptide linkage
(d) Maltose is a reducing sugar
Answer
Answer: (c) In sucrose the two monosaccharides are held together by peptide linkage
Question 21.
In cellulose, D-glucose units are joined by
(a) α-1, 4 glycosidic linkage
(b) β-1, 6 glycosidic linkage
(c) β-1, 4 glycosidic linkage
(d) peptide linkage
Answer
Answer: (c) β-1, 4 glycosidic linkage
Question 22.
The anomeric carbon in D (+) glucose is
(a) C-1 carbon
(b) C-2 carbon
(c) C-5 carbon
(d) C-6 carbon
Answer
Answer: (a) C-1 carbon
Question 23.
Glucose ![]() Product is
Product is
(a) hexanoic acid
(b) gluconic acid
(c) saccharic acid
(d) bromohexane
Answer
Answer: (b) gluconic acid
Question 24.
How many C-atoms are there is a pyranose ring?
(a) 3
(b) 5
(c) 6
(d) 7
Answer
Answer: (c) 6
Question 25.
Cellulose is a
(a) hexapolysaccharide
(b) pentapolysaccharide
(c) tripolysaccharide
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 26.
The letter ‘D’ in carbohydrates signifies
(a) dextrorotatory
(b) configuration
(c) diamagnetic nature
(d) mode of synthesis
Answer
Answer: (b) configuration
Question 27.
A diabetic person carries a packet of glucose with him always, because
(a) glucose increases the blood sugar level slowly
(b) glucose reduces the blood sugar level
(c) glucose increases the blood sugar level almost instantaneously
(d) glucose reduces the blood sugar level slowly
Answer
Answer: (c) glucose increases the blood sugar level almost instantaneously
Question 28.
Among the naturally occurring carbohydrates, furanose ring is found in the
(a) Glucose unit of cane sugar
(b) Glucose unit of cellulose
(c) Fructose unit of cane sugar
(d) Galactose unit of lactose
Answer
Answer: (c) Fructose unit of cane sugar
Question 29.
The given structure (I) and (II) represent configuration of the simplest sugar glyceraldehyde. Which of the following statements is not correct for the structures?
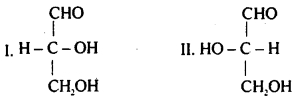
(a) I represents D-form while II represents L-form of glyceraldehyde
(b) The sugars having same configuration as D- glyceraldehyde are designated as D-sugars
(c) Natural glucose and fructose are D-forms
(d) D is dextrorotatory while L is laevorotatory enatiomer
Answer
Answer: (d) D is dextrorotatory while L is laevorotatory enatiomer
Question 30.
Amino acids generally exist in the form of Z witter ions. This means they contain
(a) Basic – NH2 group and acidic – COOH group
(b) The basic – NH3 group and acidic – COO– group
(c) Basic -NH2 and acidic – H+ group
(d) Basic – COO– group and acidic – NH3 group
Answer
Answer: (d) Basic – COO– group and acidic – NH3 group
Question 31.
Globular proteins are present in
(a) blood
(b) eggs
(c) milk
(d) all of these
Answer
Answer: (d) all of these
Question 32.
Which one of the amino acids can be synthesised in the body?
(a) Alanine
(b) Lysine
(c) Valine
(d) Histidine
Answer
Answer: (a) Alanine
Question 33.
Which of the following is not true about amino acids?
(a) They are constituents of all proteins
(b) Alanine having one amino and one carboxylic group
(c) Most naturally occurring amino acids have D-configuration
(d) Glycine is the only naturally occuring amino acid which is optically inactive.
Answer
Answer: (c) Most naturally occurring amino acids have D-configuration
Question 34.
A compound which contains both ………… and ………… is called amino acid. The amino acids is polypeptide chain are joined by ………/ bonds.
(a) amino, carboxylic group, ester
(b) amino, carboxylic group, peptide
(c) nitrogen, carbon, glycosidic
(d) hydroxy, carboxylic group, peptide
Answer
Answer: (b) amino, carboxylic group, peptide
Question 35.
Denaturation of protein leads to loss of its biological activity by
(a) formation of amino acids
(b) loss of primary structure
(c) loss of both primary and secondary structure
(d) loss of both secondary and tertiary structures
Answer
Answer: (d) loss of both secondary and tertiary structures
Question 36.
Proteins are condensation polymers of
(a) α-amino acids
(b) β-amino acids
(c) α-hydroxy acids
(d) β-hydroxy acids
Answer
Answer: (a) α-amino acids
Question 37.
Mark the wrong statement about denaturation of proteins
(a) The primary structure of the protein does not change
(b) Globular proteins are converted into fibrous proteins
(c) Fibrous proteins are converted into globular proteins
(d) The biological activity of the protein is destroyed
Answer
Answer: (c) Fibrous proteins are converted into globular proteins
Question 38.
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together
(a) van der waals forces
(b) electrostatic forces of attraction
(c) hydrogen bonds
(d) covalent bonds
Answer
Answer: (c) hydrogen bonds
Question 39.
Which type of interactions are responsible for making the a-helix structure stable?
(a) Peptide bonds between -NH2 and -CO groups of adjacent carbon chain
(b) Hydrogen bonds between -NH of amino acid in the one turn with -CO of amino acid to adjacent turn
(c) -OH group of one amino acid with -CO group of other amino acid on the turn
(d) Hydrogen bonds between adjacent amino acids
Answer
Answer: (b) Hydrogen bonds between -NH of amino acid in the one turn with -CO of amino acid to adjacent turn
Question 40.
Secondary structure of protein refers to
(a) sequence of amino acids in polypeptide chain
(b) bonds between alternate polypeptide chains
(c) folding patterns of polypeptide chain
(d) bonding between NH\(_{3}^{+}\) and COO– of two peptides
Answer
Answer: (c) folding patterns of polypeptide chain
Question 41.
Which compound can exist in a dipolar (zwitter ion) structure?
(a) C6H5CH2CH (N = CH2) COOH
(b) (CH3)2CHCH (NH2) COOH
(c) C6H5CONHCH2COOH
(d) HOOCCH2CH2COCOOH
Answer
Answer: (b) (CH3)2CHCH (NH2) COOH
Question 42.
Which of the following is an acidic amino acid?
(a) Glycine
(b) Valine
(c) Leucine
(d) Glutamic acid
Answer
Answer: (d) Glutamic acid
Question 43.
The melting points of amino acids are higher than the corresponding hal-acids because
(a) amino acids exist as zwitter ions resulting in strong dipole-dipole attraction
(b) amino acids are optically active
(c) due to higher molecular mass of-NH2 group molecular mass of amino acids is higher
(d) they interact with water more than halo-acids and have salt like structure
Answer
Answer: (a) amino acids exist as zwitter ions resulting in strong dipole-dipole attraction
Question 44.
Most common types of secondary structures of proteins are
(a) a-helix and P-helix structures
(b) a-helix and P-pleated sheet structures
(c) right and left hand twisted structures
(d) globular and fibrous structures
Answer
Answer: (b) a-helix and P-pleated sheet structures
Question 45.
Mark the incorrect example
(a) Keratin and myosin-fibrous proteins
(b) Insulin and albumines-Globular proteins
(c) Glycylalanine-Djpeptide
(d) Enzymes and haemoglobin-Derived proteins
Answer
Answer: (d) Enzymes and haemoglobin-Derived proteins
0 Comments