MCQ Questions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions with Answers
Students are advised to solve the Trigonometric Functions Multiple Choice Questions of Class 11 Maths to know different concepts. Practicing the MCQ Questions on Trigonometric Functions Class 11 with answers will boost your confidence thereby helping you score well in the exam.
Explore numerous MCQ Questions of Trigonometric Functions Class 11 with answers provided with detailed solutions by looking below.
Question 1.
The value of sin 15 + cos 15 is
(a) 1
(b) 1/2
(c) √3/2
(d) √3
Answer
Answer: (c) √3/2
Given, sin 15 + cos 15
= sin 15 + cos(90 – 15)
= sin 15 + sin 15
= 2 × sin 45 × cos 30
= 2 × (1/√2) × (√3/2)
= √3/2
Question 2.
The value of tan A/2 – cot A/2 + 2cot A is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) -1
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) 0
Given, tan A/2 – cot A/2 + 2cot A
= {sin(A/2)/cos(A/2)} – {cos(A/2)/sin(A/2)} + 2cotA
= {sin² (A/2) – cos² (A/2)}/{cos(A/2) × sin(A/2)} + 2cotA
= -{cos² (A/2) – sin² (A/2)}/{cos(A/2) × sin(A/2)} + 2cotA
= -{cosA}/{cos(A/2) × sin(A/2)} + 2cotA (since cos² A – sin² A = cos²A )
= -{cos(2A/2)}/{cos(A/2) × sin(A/2)} + 2cotA
= -{2 × cosA}/{2 × cos(A/2) × sin(A/2)} + 2cotA
= -{2cosA}/{sin(2A/2)} + 2cotA
= {-(2cosA)/(sinA)} + 2cotA (since sin2A = 2 × sinA × cosA)
= -2cotA + 2cotA
= 0
Question 3.
The value of 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) is
(a) sin x
(b) sin 2x
(c) sin 3x
(d) sin 4x
Answer
Answer: (c) sin 3x
Given, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3)
= 4 × sin x × {sin x × cos π/3 + cos x × sin π/3} × {sin x × cos 2π/3 + cos x × sin 2π/3}
= 4 × sin x × {(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2} × {-(sin x)/2 + (√3 × cos x)/2}
= 4 × sin x × {-(sin² x)/4 + (3 × cos² x)/4}
= sin x × {-sin² x + 3 × cos² x}
= sin x × {-sin² x + 3 × (1 – sin² x)}
= sin x × {-sin² x + 3 – 3 × sin² x}
= sin x × {3 – 4 × sin² x}
= 3 × sin x – 4sin³ x
= sin 3x
So, 4 × sin x × sin(x + π/3) × sin(x + 2π/3) = sin 3x
Question 4.
If tan x = (cos 9 + sin 9)/(cos 9 – sin 9), then x =
(a) 45
(b) 54
(c) 36
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) 54
Given, tan x = (cos 9 + sin 9)/(cos 9 – sin 9)
⇒ tan x = {cos 9(1 + sin 9/cos 9)}/{cos 9(1 – sin 9/cos 9)}
⇒ tan x = (1 + tan 9)}/(1 – tan 9)
⇒ tan x = (tan 45 + tan 9)}/(1 – tan 45 × tan 9) {since tan 45 = 1}
⇒ tan x = tan(45 + 9) {Apply tan(A + B) formula}
⇒ tan x = tan(54)
⇒ x = 54
Question 5.
In a triangle ABC, sin A – cos B = cos C, then angle B is
(a) π/2
(b) π/3
(c) π/4
(d) π/6
Answer
Answer: (a) π/2
Given, sin A – cos B = sin C
⇒ sin A = cos B + sin C
⇒ 2 × sin (A/2) × cos (A/2) = 2 × cos {(B + C)/2} × cos {(B – C)/2}
⇒ 2 × sin (A/2) × cos (A/2) = 2 × cos {π/2 – A/2} × cos {(B – C)/2}
⇒ 2 × sin (A/2) × cos (A/2) = 2 × sin (A/2) × cos {(B – C)/2}
⇒ cos (A/2) = cos {(B – C)/2}
⇒ A/2 = (B – C)/2
⇒ A = B – C
⇒ B = A + C
⇒ B = π – B {Since A + B + C = π}
⇒ 2B = π
⇒ B = π/2
Question 6.
The value of cos 420° is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 1/2
(d) √3/2
Answer
Answer: (c) 1/2
cos 420° = cos(360° + 60° ) = cos 60° = 1/2
Question 7.
If in a triangle ABC, tan A + tan B + tan C = 6 then the value of cot A × cot B × cot C is
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/3
(c) 1/4
(d) 1/6
Answer
Answer: (d) 1/6
Given tanA + tanB + tanC = 6
Now tan(A + B + C) = {(tanA + tanB + tanC) – tanA × tanB × tanC}/{1 – (tanA × tanB + tanB × tanC + tanA × tanC)}
We know that,
A + B + C = π
⇒ tan(A + B + C) = tan π
⇒ tan(A + B + C) = 0
Now
0 = {(tanA + tanB + tanC) – tanA × tanB × tanC}/{1 – (tanA × tanB + tanB × tanC + tanA × tanC)}
⇒ tanA + tanB + tanC – tanA × tanB × tanC = 0
⇒ tanA + tanB + tanC = tanA × tanB × tanC
⇒ tanA × tanB × tanC = 6
⇒ (1/cotA) × (1/cotB) × (1/cotC) = 6
⇒ 1/(cot A × cot B × cot C) = 6
⇒ cot A × cot B × cot C = 1/6
Question 8.
If a × cos x + b × cos x = c, then the value of (a × sin x – b × cos x)² is
(a) a² + b² + c²
(b) a² – b² – c²
(c) a² – b² + c²
(d) a² + b² – c²
Answer
Answer: (d) a² + b² – c²
We have
(a × cos x + b × sin x)² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b²
⇒ c² + (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b²
⇒ (a × sin x – b × cos x)² = a² + b² – c²
Question 9.
When the length of the shadow of a pole is equal to the height of the pole, then the elevation of source of light is
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 75°
(d) 45°
Answer
Answer: (d) 45°
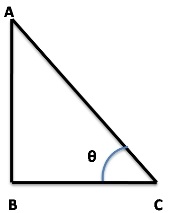
Let AB is the length of the pole and BC is the shadow of the pole.
Given AB = BC
Now from triangle ABC,
tan θ = AB/BC
⇒ tan θ = 1
⇒ θ = 45°
So, the elevation of source of light is 45°
Question 10.
In any triangle ABC, if cos A/a = cos B/b = cos C/c and the side a = 2, then the area of the triangle is
(a) √3
(b) √3/4
(c) √3/2
(d) 1/√3
Answer
Answer: (a) √3
Given cos A/a = cos B/b = cos C/c
= cos A/k × sin A = cos B/k × sin B = cos C/k × sin C {since sin A/a = sin B/b = sin C/c = k}
= cot A = cot B = cot C
⇒ A = B = C = 60
So, triangle ABS is equilateral.
Now area of the triangle = (√3/4) × a² = (√3/4) × 2² = (√3/4) × 4 = √3
Question 11.
The least values of cos² θ + sec² θ is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) more than 2
Answer
Answer: (c) 2
If a × cos² θ + b × sec² θ is given,
then the least value = 2√ab
Now given, cos² θ + sec² θ
Here, a = 1, b = 1
Now, least value = 2√(1 × 1) = 2 × 1 = 2
Question 12.
The equation (cos p – 1) x² + cos p × x + sin p = 0, where x is a variable, has real roots. Then the interval of p may be any one of the following:
(a) (0, π)
(b) (−π/2, π/2)
(c) (0, π)
(d) (−π, 0)
Answer
Answer: (a) (0, π)
The equation (cos p – 1)
x² + cos p × x + sin p = 0, where x is a variable, has real roots.
Now, for real roots,
Discriminant ≥ 0
⇒ cos² p – 4(cosp – 1)sinp ≥ 0
⇒ (cosp – 2sinp)² – 4sin² p + 4sinp ≥ 0
⇒ (cosp – 2sinp)² + 4sin p(1 – sinp) ≥ 0 ………..1
Now, 1 – sinp ≥ 0
⇒ For all real p such that 0 < p < π
So that 4sin p(1 – sinp) ≥ 0
So, p ∈ (0, π)
Question 13.
The value of (sec 8A – 1)/(sec 4A – 1) is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) tan 8A/tan 2A
(d) tan 2A/tan 8A
Answer
Answer: (c) tan 8A/tan 2A
Given, (sec 8A – 1)/(sec 4A – 1)
= (1/cos 8A – 1)/(1/cos 4A – 1)
= {(1 – cos 8A)/cos 8A}/{(1 – cos 4A)/cos 4A}
= {(1 – cos 8A) × cos 4A}/{(1 – cos 4A) × cos 8A}
= (2sin² 4A × cos 4A}/{2sin² 2A × cos 8A} {since cos 2A = 1 – 2sin² A}
= (2sin 4A × sin 4A × cos 4A}/{2sin 2A × sin 2A × cos 8A}
= (sin 8A × sin 4A}/{2sin 2A × sin 2A × cos 8A} {since sin 2A = 2×sin A × cos A}
= (sin 8A × 2sin 2A × cos 2A}/{2sin 2A × sin 2A × cos 8A}
= (sin 8A × cos 2A}/{sin 2A × cos 8A}
= (sin 8A/cos 8A)/(sin 2A/cos 2A)
= tan 8A/tan 2A
So, (sec 8A – 1)/(sec 4A – 1) = tan 8A/tan 2A
Question 14.
The value of (sin7x + sin5x) /(cos7x + cos5x) + (sin9x + sin3x) / (cos9x + cos3x) is
(a) tan6x
(b) 2 tan6x
(c) 3 tan6x
(d) 4 tan6x
Answer
Answer: (b) 2 tan6x
Given, (sin7x + sin5x) /(cos7x + cos5x) + (sin9x + sin3x) / (cos9x + cos3x)
⇒ [{2×sin(7x + 5x)/2 × cos(7x – 5x)/2}/{2 × cos(7x + 5x)/2 × cos(7x – 5x)/2}] +
[{2×sin(9x + 3x)/2 × cos(9x – 3x)/2}/{2 × cos(9x + 3x)/2 × cos(9x – 3x)/2}]
⇒ [{2 × sin6x × cosx}/{2 × cos6x × cosx}] + [{2 × sin6x × cosx}/{2 × cos6x × cosx}]
⇒ (sin6x/cos6x) + (sin6x/cos6x)
⇒ tan6x + tan6x
⇒ 2 tan6x
Question 15.
If x > 0 then the value of f(x) = -3 × cos√(3 + x + x²) lie in the interval
(a) [-1, 1]
(b) [-2, 2]
(c) [-3, 3]
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) [-3, 3]
Given x > 0 then 3 + x + x² > 0
Now, -1 ≤ cos√(3 + x + x² ) ≤ 1 {Since -1 ≤ cosx ≤ 1}
⇒ 3 ≥ -3 × cos√(3 + x + x² ) ≥ -3 {Multiply by -3}
⇒ -3 ≤ f(x) ≤ 3
⇒ f(x) ∈ [-3, 3]
Question 16.
The value of cos 4A – cos 4B is
(a) (cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
(b) 2(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
(c) 4(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
(d) 8(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
Answer
Answer: (d) 8(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
Given, cos 4A – cos 4B
= 2cos² 2A – 1 – (2cos2 2B – 1) {since 2cos² x – 1 = cos 2x}
= 2cos² 2A – 1 – 2cos² 2B + 1
= 2cos² 2A – 2cos² 2B
= 2(cos² 2A – cos² 2B)
= 2(cos 2A – cos 2B) × (cos 2A + cos 2B)
= 2{2cos² A – 1 – (2cos² B – 1)} × {2cos² A – 1 + 1 – 2sin² B} {since 1 – 2sin² x = cos 2x}
= 2{2cos² A – 1 – 2cos² B + 1} × {2cos² A – 1 + 1 – 2sin² B}
= 2{2cos² A – 2cos² B} × {2cos² A – 2sin² B}
= 2 × 2 × 2{cos² A – cos² B} × {cos² A – sin² B}
= 8(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cos A + sin B)
So, cos 4A – cos 4B = 8(cos A – cos B) × (cos A + cos B) × (cos A – sin B) × (cosA + sin B)
Question 17.
The value of cos 420° is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 1/2
(d) √3/2
Answer
Answer: (c) 1/2
cos 420° = cos(360° + 60° ) = cos 60° = 1/2
Question 18.
In a ΔABC, (b + c) cos A + (c + a) cos B + (a + b) cos C is equal to
(a) a + b + c
(b) 0
(c) none of these
(d) Rr
Answer
Answer: (a) a + b + c
Given (b + c) cos A + (c + a) cos B + (a + b) cos C
= b × cos A + c × cos A + c × cos B + a × cos B + a × cos C + b × cos C
= (b × cos C + c × cos B) + (c × cos A + a × cos C) + (b × cos A + a × cos B)
= a + b + c {since b × cos C + c × cos B = a, c × cos A + a × cos C = b, b × cos A + a × cos B = c}
Question 19.
tan² θ = 1 – a² then the value of sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ is
(a) (2 – a²)
(b) (2 – a²)1/2
(c) (2 – a²)3/2
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) (2 – a²)3/2
Given, tan² θ = 1 – a²
⇒ tan θ = √(1 – a²)

From the figure and apply Pythagorus theorem,
AC² = AB² + BC²
⇒ AC² = {√(1 – a²)}² + 12
⇒ AC² = 1 – a² + 1
⇒ AC² = 2 – a²
⇒ AC = √(2 – a²)
Now, sec θ = √(2 – a²)
cosec θ = √(2 – a²)/√(1 – a²)
and tan θ = √(1 – a²)
Given, sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ
= √(2 – a²) + {(1 – a²)3/2 × √(2 – a²)/√(1 – a²)}
= √(2 – a²) + {(1 – a²) × (1 – a²) × √(2 – a²)/√(1 – a²)}
= √(2 – a²) + (1 – a²) × √(2 – a²)
= √(2 – a²) × (1 + 1 – a²)
= √(2 – a²) × (2 – a²)
= (2 – a²)3/2
So, sec θ + tan³ θ × cosec θ = (2 – a²)3/2
Question 20.
The value of cos(π/7) × cos(2π/7) × cos(4π/7) is
(a) -1/2
(b) -1/4
(c) -1/6
(d) -1/8
Answer
Answer: (d) -1/8
We know that cos A × cos 2A × cos 2² A × ……………… × cos 2n-1 A = sin (2ⁿ A)/{2ⁿ × sin A} ……………1
Given, cos(π/7) × cos(2π/7) × cos(4π/7)
= cos(π/7) × cos(2π/7) × cos(2² π/7)
= [sin (2³ × π/7) ]/{2³ × sin (π/7)} ……………..from equation 1
= [sin (8π/7) ]/{8 × sin (π/7)}
= [sin (π + π/7) ]/{8 × sin (π/7)}
= -sin (π/7)/{8 × sin (π/7)}
= -1/8
So, cos(π/7) × cos(2π/7) × cos(4π/7) = -1/8
0 Comments