MCQ Questions for Class 12 Physics Chapter 4 Moving Charges and Magnetism with Answers
Question 1.
The current sensitibility of a moving coil galanometer increases with decrease in:
(a) magnetic field
(b) area of a coil
(c) number of turns
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 2.
A current carring coil is placed in a uniform magnetic field. If the coil turns through an angle θ, then the torque is directly proportional to:
(a) sin θ
(b) cos θ
(c) cot θ
(d) tan θ
Answer
Answer: (b) cos θ
Question 3.
The sensitivity of a tangent galvanometer can be increased by increasing:
(a) the radius of the coil
(b) the external magnetic field
(c) the number of turns of the coil
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (b) the external magnetic field
Question 4.
The permeability of a paramagnetic substance is:
(a) very large
(b) small but more than unity
(c) less than unity
(d) negative
Answer
Answer: (b) small but more than unity
Question 5.
Which of the following shows that the earth behaves as a magnet?
(a) Repulsion between like poles .
(b) Attraction between unlike poles
(c) Null points in the magnetic field of a bar magnet
(d) No existence of isolated magnetic poles
Answer
Answer: (c) Null points in the magnetic field of a bar magnet
Question 6.
What is the angle of dip at the magnetic poles ?
(a) 30°
(b) 0°
(c) 45°
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 7.
A charged particle of mass m and charge q travels on a circular path of radius r i.e., perpendicular to the magnetic field B. The time taken by particle to complete on revolution is :
(a) \(\frac{2πqB}{m}\)
(b) \(\frac{2πm}{qB}\)
(c) \(\frac{2πmq}{B}\)
(d) \(\frac{2πq^2B}{m}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\frac{2πm}{qB}\)
Question 8.
Circular loop of radius 0.0157 m carries a current 2 A. The magnetic field at the centre of the loop is :
(a) 1.57 × 10-3Wb/m²
(b) 8.0 × 10-5 Wb/m²
(c) 2.0 × 10-3 Wb/m²
(d) 3.l4 × 10-1 Wb/m²
Answer
Answer: (b) 8.0 × 10-5 Wb/m²
Question 9.
What happens to the magnetic field at the centre of a circular current carrying coil if we double the radius of the coil keeping the current unchanged?
(a) halved
(b) doubled
(c) quadrupled
(d) remains unchanged
Answer
Answer: (a) halved
Question 10.
When we double the radius of a coil keeping the current through it unchanged, what happens to the magnetic field directed along its axis at far off points?
(a) halved
(b) doubled
(c) quadrupled
(d) remains unchanged
Answer
Answer: (d) remains unchanged
Question 11.
The strength of the magnetic field around an infinite current carrying conductor is :
(a) same everywhere
(b) inversely proportional to the distance
(c) directly proportional to the distance
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) inversely proportional to the distance
Question 12.
A current carrying power line carries current from west to east. Then the direction of the magnetic field 2 m above it is :
(a) west to east
(b) south to north
(c) north to south
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) north to south
Question 13.
According to Ampere’s Circuital law

Answer
Answer: (b)
Question 14.
The force between two parallel current carrying conductors is F. If the current in each conductor is doubled, then the force between them becomes :
(a) 4F
(b) 2F
(c) F
(d) \(\frac{F}{4}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) 4F
Question 15.
How much force will be experienced by a moving charge in a magnetic field? The symbols have their usual meanings.
(a) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\).\(\vec{B}\))
(b) \(\vec{F}\) = \(\frac{q}{(\vec{v}.\vec{B})}\)
(c) \(\vec{F}\) = \(\frac{q}{2}\)\((\vec{v}×\vec{B}\))
(d) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\)×\(\vec{B}\))
Answer
Answer: (d) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\)×\(\vec{B}\))
Question 16.
Which of the following is not a unit of magnetic induction?
(a) gauss
(b) tesla
(c) oersted
(d) weber/metre²
Answer
Answer: (c) oersted
Question 17.
The magnetic field produced by an / meter long straight (x cry thin) current (I) carry ing conductor at any point on itself is :
(a) zero
(b) infinite
(c) \(\frac{µ_0l}{4πl}\)
(d) \(\frac{µ_0l}{2πl}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) zero
Question 18.
A charge + q is sent through a magnetic field. The force acting on it is maximum w hen the angle between the direction of motion of the charged particle and the magnetic field :
(a) 0°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 180°
Answer
Answer: (c) 90°
Question 19.
An electron having mass ‘m’ and Kinetic energy E enters in uniform magnetic field B perpendicular, then its frequency will be:
(a) \(\frac{eE}{qmB}\)
(b) \(\frac{2πm}{eB}\)
(c) \(\frac{eB}{2πm}\)
(d) \(\frac{2m}{eBE}\)
Answer
Answer: (c) \(\frac{eB}{2πm}\)
Question 20.
A wire of length 2 metre carries a current 1 ampere, is bent to form a circle. The magnetic moment of the coil is :
(a) 2π
(b) π/2
(c) π/4
(d) 1/π
Answer
Answer: (d) 1/π
Question 21.
The magnetic field of a given length of a ware for single turn coil at its centre is B. Then.its value for two turns of coil will be :
(a) B/4
(b) B/2
(c) 4B
(d) 2B
Answer
Answer: (c) 4B
Question 22.
When charged particle enters-a uniform magnetic field, its K.E.:
(a) remains constant
(b) increases
(c) decreases
(d) becomes zero
Answer
Answer: (a) remains constant
Question 23.
To convert galvanometer into voltmeter one should connect :
(a) high resistance in series with galvanometer
(b) low resistance in series with galvanometer
(c) high resistance in parallel with galvanometer
(d) low resistance in parallel with galvanometer
Answer
Answer: (a) high resistance in series with galvanometer
Question 24.
A charge q moves in a region, where electric field E and magnetic field B both exist, then force on it is :
(a) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\)×\(\vec{B}\))
(b) \(\vec{F}\) = q{\(\vec{E}\)×(\(\vec{v}\) × \(\vec{B}\))}
(c) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{E}\) + (\(\vec{B}\) × \(\vec{v}\))
(d) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{B}\) + (\(\vec{E}\) ×\(\vec{v}\))
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\vec{F}\) = q{\(\vec{E}\)×(\(\vec{v}\) × \(\vec{B}\))}
Question 25.
Isoclinic lines are the lines joining places with :
(a) equal dip
(b) equal declination
(cj equal dip and declination
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) equal dip
Question 26.
Two identical bar magnets each of dipole moment p and length I are perpendicular to each other as shown in Fig. The dipole moment of the combination is:
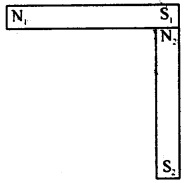
(a) √2 p
(b) \(\frac{p}{√2}\)
(c) P
(d) 2p
Answer
Answer: (a) √2 p
Question 27.
The most suitable metal for making permanent magnets is :
(a) iron
(b) steel
(c) copper
(d) aluminium
Answer
Answer: (b) steel
Question 28.
The SI unit of magnetic dipole moment is’
(a) Ampere
(b) Ampere metre²
(c) Tesla
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Ampere metre²
Question 29.
Earth’s magnetism was discovered by:
(a) Gauss
(b) Oersted
(c) Ampere
(d) Gilbert
Answer
Answer: (d) Gilbert
Question 30.
According to Gauss’s theorem in magnetism, surface integral of magnetic field intensity over a surface (closed or open) is always:
(a) -1
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) infinity
Answer
Answer: (c) 0
Question 31.
Tesla is a unit of:
(a) electric flux
(b) magnetic flux
(c) magnetic field
(d) electric field
Answer
Answer: (c) magnetic field
Question 32.
10 eV electron is circulating in a plane at right angle to a uniform field of magnetic induction 10-1 Wb/m² (1G). The orbital radius of electron is:
(a) 12 cm
(b) 16 cm
(c) 11 cm
(d) 18 cm
Answer
Answer: (c) 11 cm
Question 33.
A cyclotron can be used to produce high energy:
(a) neutrons
(b) deutrons
(c) β particles
(d) α partifcles
Answer
Answer: (d) α partifcles
Question 34.
The radius of the trajectory of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field is proportional to the:
(a) charge on the particle
(b) energy of the particle
(c) momentum of the particle
(d) all the above
Answer
Answer: (c) momentum of the particle
Question 35.
The force \(\vec{F}\) experienced by a particle of charge q moving with velocity \(\vec{v}\) in a magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) is given by,
(a) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{F}\) × \(\vec{B}\))
(b) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{B}\) × (\(\vec{b}\))
(c) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\) × (\(\vec{B}\))
(d) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{v}\) × \(\vec{B}\))
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\vec{F}\) = q(\(\vec{F}\) × \(\vec{B}\))
Question 36.
The torque acting on a magnetic dipole of moment \(\vec{p_m}\) when placed in a magnetic field \(\vec{B}\) is:
(a) pmB
(b) \(\vec{p_m}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
(c) \(\vec{p_m}\)\(\vec{B}\)
(d) \(\frac{p_m}{B}\)
Answer
Answer: (b) \(\vec{p_m}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
Question 37.
In thomson spectrograph \(\vec{E}\) ⊥ \(\vec{B}\), then velocity of electron beam will be:
(a) |\(\vec{E}\)|/|\(\vec{B}\)|
(b) \(\vec{E}\) × \(\vec{B}\)
(c) |\(\vec{B}\)|/|\(\vec{E}\)|
(d) E² / B²
Answer
Answer: (a) |\(\vec{E}\)|/|\(\vec{B}\)|